A work breakdown structure (WBS) helps you visualize all your project tasks, making it easier to allocate resources, track progress and improve scheduling.
In this article, you’ll learn what work breakdown structures are and why you should use them. You’ll also discover the key components of a work breakdown structure, learn the six steps for building your own and find a list of helpful work breakdown structure software.
Key takeaways from work breakdown structure
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a document or chart that breaks a project into smaller, manageable phases and tasks.
Organizing a project’s scope into this hierarchical breakdown provides visual clarity for improved planning, resource allocation and scope control.
Create a custom WBS for any project in six steps, using WBS software to make the process easier.
Pipedrive’s project management software can help you organize and generate a WBS to share with your project team. Start now with a free 14-day trial.
What is a work breakdown structure?
A work breakdown structure (WBS) outlines all your project tasks, activities and deliverables in one location.
Project managers use the structure – popularized by The Project Management Institute’s (PMI) PMBOK Guide – to break the project scope into manageable sections
Note: The project scope defines the objectives, deliverables, boundaries and tasks needed to complete a project successfully.
A WBS divides a project into a hierarchical structure. It typically appears in a top-down format, starting with the project goal at the top.
The goal feeds into project phases (the different categories of work within the project) or deliverables. These are further broken down into an outline of all the project activities.
Here’s an example of a WBS outline:
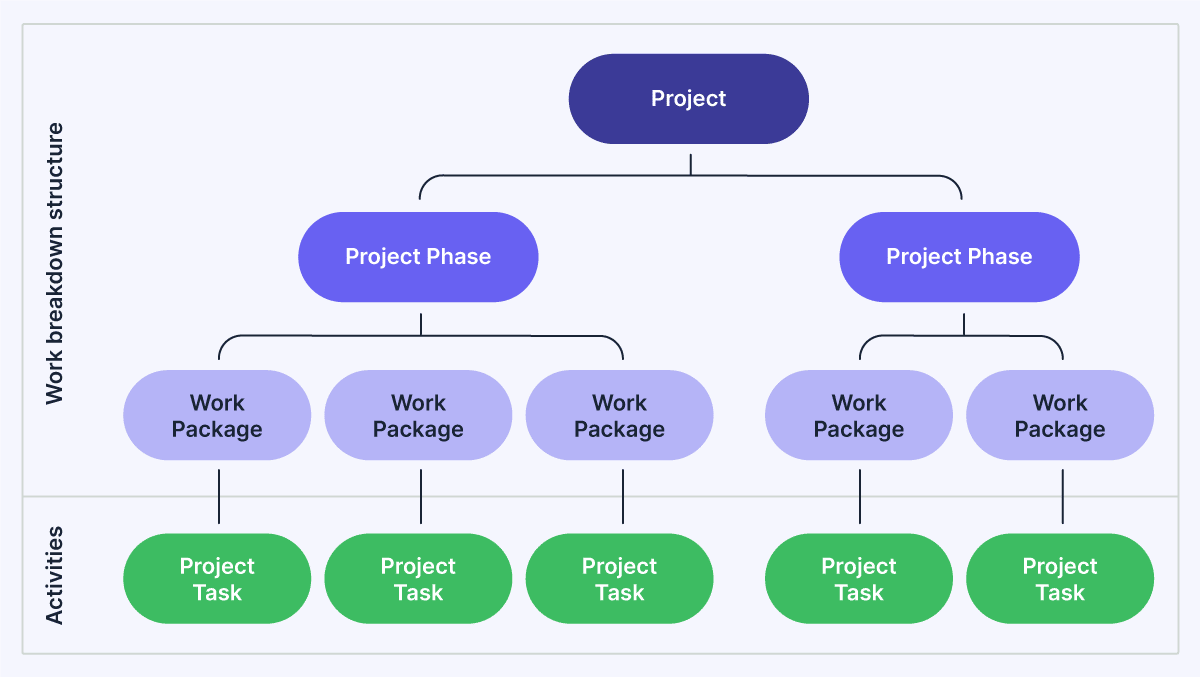
.
Note: The top-down structure is the most well-known, but you can create a WBS in different formats – like a Kanban board. In a Kanban format, each column represents a different project phase. You can add individual tasks in the relevant columns to categorize activities.
A WBS is useful for managing large-scale or complex projects. Its structure breaks everything down into manageable components, making it easier for project managers to create an accurate project schedule.
For this reason, managers often use it as part of the waterfall methodology, which divides projects into clearly defined, sequential phases.
What are the types of work breakdown structures?
There are three work breakdown structure types:
A phase-based WBS typically divides the first level of the WBS into the five elements of the project lifecycle
A deliverable-oriented WBS organizes the project into tangible outputs, breaking each down into smaller components required to complete them
A responsibility-based WBS groups tasks based on team roles, departments or individuals responsible for completing them
The ideal format depends on your specific project needs.
For instance, a phase-based WBS works well for projects with a clear lifecycle. A good example is a software development project that moves through stages such as design, development, testing and deployment.
However, a deliverable-based WBS is better for projects with tangible outputs. For example, a construction project with deliverables like foundation, framing and roofing.
What is work breakdown structure vs. schedule?
A work breakdown structure defines the scope of a project (establishing what tasks need to be done), while a schedule creates a timeline for the project, providing start and completion dates for all tasks.
Think of the WBS as the “what” of the project, and the schedule as the “when” and “how”.
The schedule outlines the sequence of tasks in a timeline or a Gantt chart. It also highlights dependencies between tasks, indicating which activities must start (or finish) for other tasks to start (or finish).
For a website development project, the project manager might create a WBS to account for all activities from a high level. They might then create a Gantt chart (like the following) to map the timeline and milestones.

Combining the schedule with the WBS makes it easier to estimate the project duration. It also helps you identify overlapping tasks, potential delays or bottlenecks.
What are key components of a work breakdown structure?
An effective work breakdown structure includes specific components that cover all the necessary project details.
Here’s an overview of the essential WBS elements:
Phases | Major stages of the project lifecycle |
Tasks | Individual activities within each phase |
Subtasks | Smaller activities that make up a task |
Depending on your project, you may also want to include the following information:
Project deliverables | The end goal of a project, as well as smaller outputs required along the way |
Work packages | A group of related tasks at the lowest level of the WBS needed to complete a sub-deliverable |
Milestones | Events that mark the completion of key phases or deliverables |
Cost estimates | Approximations of the project’s costs and resources |
Dependencies | Relationships between tasks |
Project baseline or scope statement | A statement that includes the project’s name, plan and description |
Project stakeholders | The people involved in the project |
Choose the level of detail that will break your project down as efficiently as possible.
What are the benefits of using a work breakdown structure?
A work breakdown structure helps project managers determine the scope and schedule of an upcoming project.
Here’s how a WBS can benefit your project:
Clarify the project scope. Define every aspect of the project to create a shared understanding of the project’s goals, deliverables and boundaries.
Minimize scope creep. Clarify all deliverables and tasks to prevent additional tasks from sneaking into a project unchecked.
Improve project planning and scheduling. Outline all project work to create an accurate and realistic project schedule.
Enhance project clarity. Break down projects into hierarchical, smaller tasks, ensuring everyone understands the project scope and individual responsibilities.
Reduce risks. Identify and address potential risks proactively, increasing the chance of a smooth project execution.
What are the 5 phases of a work breakdown structure?
A phase-based WBS typically breaks the first level down into the five elements of the project life cycle:
Initiation. Activities that support the initial stages of the project, like defining objectives or identifying stakeholders.
Planning. Activities involved in the planning phase, like allocating resources or conducting risk assessments.
Execution. Activities that implement the project plan, like developing deliverables.
Control. Activities that monitor and measure progress, like tracking milestones and monitoring quality.
Closeout. Activities that finalize the project, like delivering completed work and gathering feedback.
A structure like this ensures you address all critical aspects of the project lifecycle. It also aligns with how projects naturally progress, helping you organize activities logically.
Note: A phase-based WBS doesn’t have to follow the five phases of the project lifecycle. You can customize the phases based on your project’s needs and structure.
Work breakdown structure example
Look at the phase-based WBS example below for a website development project.
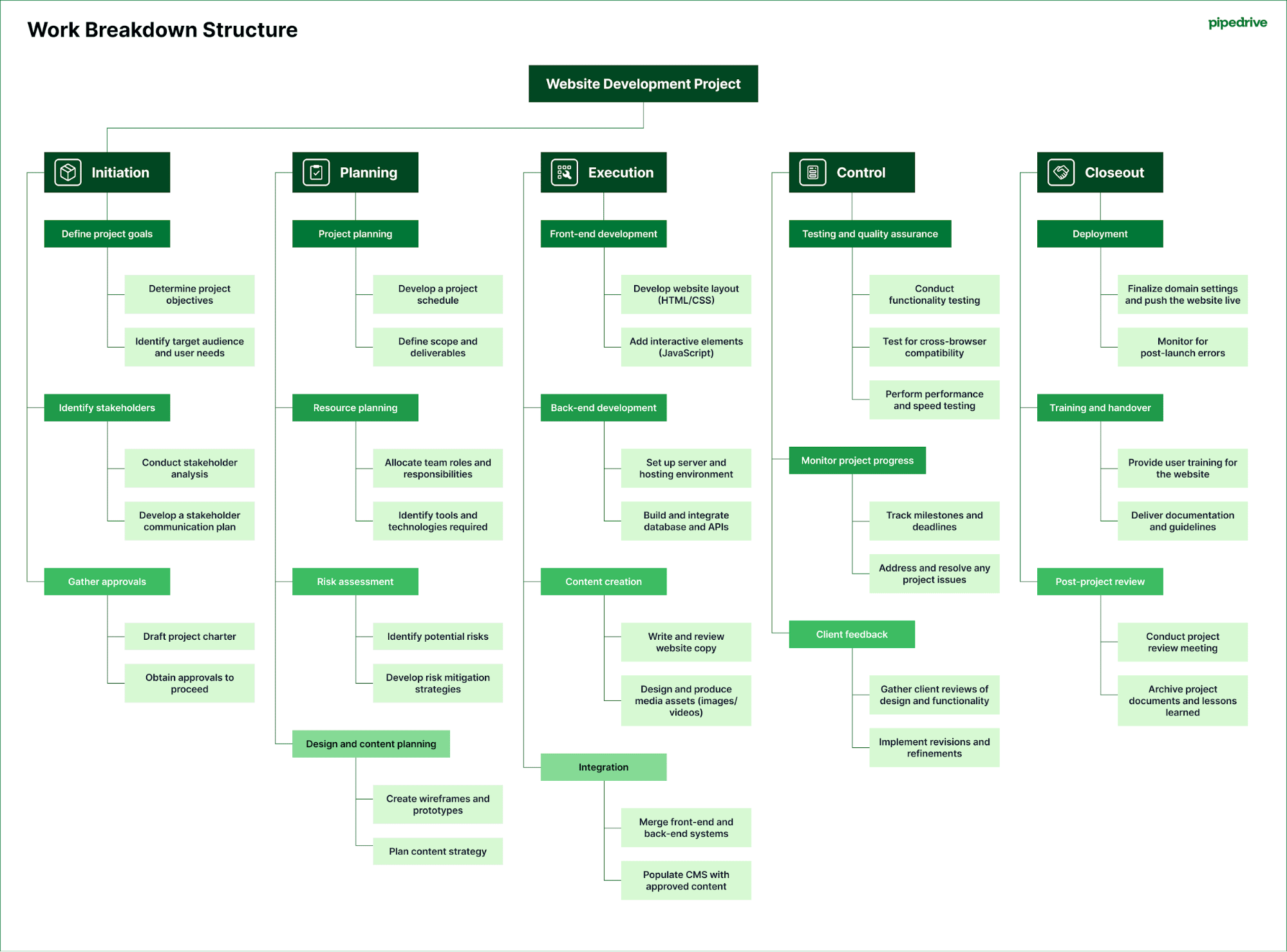
This simple WBS template organizes the project into the five project phases, clearly showing the tasks and related subtasks for each. It makes it easy to see what deliverables will be delivered and when.
How do I create a work breakdown structure? 6 simple steps
Follow these six steps to create an effective phase-based work breakdown structure.
Note: To create a deliverable- or responsibility-based WBS, follow the steps listed below, but adjust the phases and tasks accordingly. For example, instead of using phases that align with the project lifecycle, create phases based solely on deliverables or responsibilities.
1. Define the project scope
The project scope outlines your main objectives, key deliverables and boundaries.
Here’s how to define your project scope:
Define the main objectives and what the project aims to achieve
Describe the required deliverables and expected outcomes
Set boundaries by stating what activities the project will and won’t include
Clarify any project constraints, like budgets or timeline requirements
Put all of this information into a project scope statement.
Here’s an example of a project scope statement for a new product launch:
Project objectives |
|
Deliverables |
|
In-scope activities |
|
Out-of-scope activities |
|
Constraints |
|
Feel free to use this project scope template and customize it as needed.
2. Identify key phases
Break the project into major phases representing core project components or milestones.
Choose phases that reflect your project's natural progression. You can use the five project phases (initiation, planning, execution, control and closeout) or create phases relevant to your project.
To decide which option to use, think about how best to group your project activities.
Say you’re managing a software development project. If you feel limited by the five project phases, you might create custom phases that better align with your specific activities and deliverables. Here are some examples of what those phases might be:
Phase 1 – Concept exploration (brainstorming, idea validation and feasibility analysis)
Phase 2 – Requirements definition and prototyping (collecting detailed requirements and developing a functional prototype)
Phase 3 – Architectural design and planning (creating the software’s high-level structure and technical roadmap)
Phase 4 – Iterative development (developing, testing and refining features in agile sprints or incremental cycles)
Phase 5 – User experience testing (conducting usability tests, gathering user feedback and making improvements)
Phase 6 – Pre-deployment readiness (final quality assurance, scalability testing and deployment environment setup)
Phase 7 – Continuous improvement (monitoring performance and implementing updates based on user feedback)
Note: When identifying phases, focus on tangible outcomes instead of actions. Phases should represent the project’s key deliverables rather than the specific actions taken to produce them.
For example, in a marketing campaign, instead of creating phases for things like “creating ad copy” or “designing graphics”, focus on outcomes like “producing creative assets”.
3. Break deliverables into smaller tasks
List deliverables for each phase and then divide them into smaller, manageable tasks (also known as sub-deliverables).
By the end of this step, you’ll have a clear outline of all the activities you must complete to execute the project.
To outline sub-deliverables, identify the key activities required to complete each phase. Here are the activities you might include in the initiation phase of a market research project:
Gather research requirements
Identify data sources
Conduct initial market research
Develop a project charter
Gain initiation phase approval
From here, you might break the project down further and create work packages. For instance, for the sub-deliverable “identify data sources”, your work package might include the following activities:
Decide on qualitative or quantitative methods
Research secondary data sources (industry reports, existing surveys)
Identify potential primary data sources (surveys, focus groups)
Better understand your customers with our Buyer Persona Templates
4. Add tasks to a project management tool
Use project management software to organize and structure your WBS.
These tools make it easy to add tasks, arrange them in a hierarchy and share the WBS when it’s finished.
Here are some of the features to look for in a project management tool:
Offers multiple views. Different views help you visualize tasks in the WBS format that works best for your team, like a Gantt chart or tree diagram.
Integrates with other tools. Integrations enable seamless communication and data sharing between all your systems, helping you create efficient project workflows.
Provides online access. A cloud-based tool gives project team members real-time access to the most up-to-date WBS at any time.
Note: Some project managers use Microsoft Excel to create their WBS. However, a project management tool makes it easier to make changes, share real-time updates and collaborate with team members when finalizing the WBS.
5. Choose the ideal WBS format
Choose the type of WBS that suits the project’s complexity and objectives.
Selecting the right format ensures you outline all the project tasks effectively.
Consider the complexity of your project and what you want to outline in the WBS. Answering these questions will help you choose the best format for it.
For example, creating your WBS as a Gantt chart might be the best option for planning a project with complex dependencies and timelines. The classic tree diagram is the best fit if you’re planning a project with multiple layers of deliverables.
6. Organize tasks into a hierarchy
Structure the WBS into hierarchical levels, starting with high-level deliverables in each phase. From here, add the tasks, subtasks and work packages.
Say you’re creating a WBS for a marketing campaign project. Under a high-level deliverable like “content creation”, you might add the following tasks:
Write blog posts
Design social media graphics
Produce video content
Under “write blog posts”, you might include the following subtasks:
Research topics
Outline content
Draft blog posts
Some work breakdown structures use a numbering system for further clarity when organizing tasks. Here’s an example of how this works:
1. Website development | |
1.1. Design | 1.1.1. Create wireframes 1.1.2. Develop mockups 1.1.3. Approve final design |
1.2. Content creation | 1.2.1. Write website copy 1.2.2. Review and edit content 1.2.3. Select and produce media |
1.3. Development | 1.3.1. Front-end coding 1.3.2. Back-end coding 1.3.3. Integrate front-end and back-end |
5 top work breakdown structure tools
The right software can help you visualize and organize large projects and automate routine tasks, such as triggering notifications as tasks are completed.
From comprehensive project management software to team-based diagraming platforms, here are five top WBS tools to consider.
1. Pipedrive
Pipedrive’s Projects feature combines overall project management with sales-focused tools. The intuitive interface makes it easy to create hierarchies and customize your project work breakdown structure to suit your needs.
Here’s how to create a WBS in Pipedrive:
Start by creating a project. Click the “Projects” tab on the left of the main projects page.

In the “Add project” dialog, fill out the options as follows:
Select template – choose a premade or custom project framework
Title – the title of your project
Start and end date – the start and end dates of your project
Board – the group of projects this will be added to
Phase – the project stages of your WBS
Owner – the Pipedrive user who owns the project
Deal, person, organization – the deal, person and organization linked to the project
Labels – any labels applied to your project
Description – a short description of your project
Next, choose your ideal WBS format. You can choose a board view (Kanban) or, you can choose the list view:
Add tasks to your project using the “+ Task” button under the plan tab, assigning each task to a project phase.
Alternately, you can click the “+ Task” option below a project phase to add tasks directly to it:
Clicking “+ Task” opens the contextual view, where you can provide the following information:
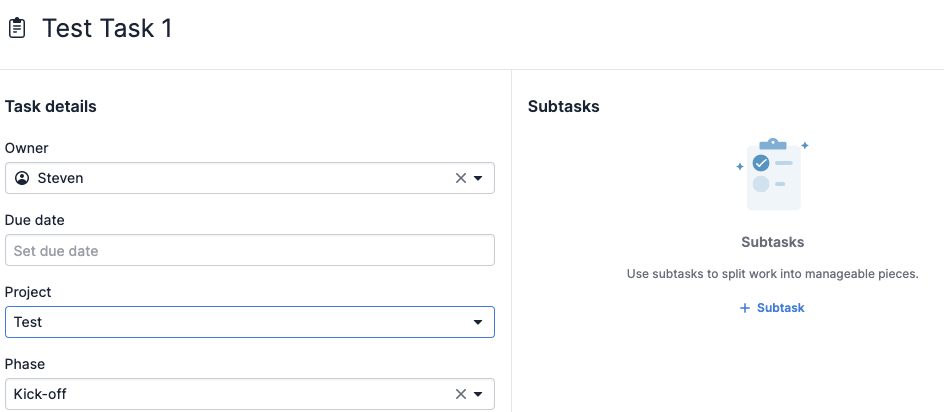
Hit “Save”, and the task will appear in your project.
Pipedrive is a great tool for organizing and tracking project progress from start to finish.
Key features:
Task organization. Create tasks and subtasks for a project and organize them into different phases.
Visual workflows. Use customizable Kanban-style boards to organize project phases.
Integration with the sales process. Create a project directly from a deal and carry over relevant customer data.
Automation. Automate repetitive tasks like sending reminders or updating a task’s status.
Who it’s best for: Pipedrive is an excellent option for organizations that need to manage projects within the context of their sales, as it can directly connect projects to customer data and the sales pipeline.
2. ClickUp
ClickUp is an all-in-one work management platform that combines project management, task management, documents, time tracking and automation into a single application.
Source: Clickup
The platform provides a flexible, hierarchical structure and offers features that help you keep your team on the same page throughout the project.
Key features:
Customizable views. Choose from various visual views like Gantt charts, Mind Maps and Whiteboards to cater to diverse thinking styles.
Collaboration tools. Support collaboration with task delegation and communication features that let you share progress updates and communicate effectively.
Project templates. Access templates to quickly create industry-specific work breakdown structures.
Who it’s best for: ClickUp suits teams of any size that need to manage complex projects – from small business owners and freelancers to large enterprise project managers.
3. Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a cloud-based workspace that lets you diagram projects and collaborate with other stakeholders.
Source: Lucidchart
This tool allows you to import data from spreadsheets, so information is automatically updated when the spreadsheet data changes.
Key features:
Real-time collaboration. Cloud access lets multiple team members work on the WBS simultaneously, while the commenting feature centralizes conversations and feedback in the document.
Data integration. Connect to data from sources like Google Sheets and Excel for automatic WBS chart updates.
Customization and templates. Use a library of templates and symbols to adapt your WBS to specific project needs.
Mobile accessibility. Make WBS and other project documents accessible from anywhere with a mobile app.
Who should use it: Lucidchart helps distributed teams improve project alignment with instant collaboration, communication and visual clarity.
4. SmartDraw
SmartDraw is a diagramming software that offers templates and drag-and-drop functionality for creating professional-looking visuals like flowcharts and organization charts.
Source: SmartDraw
Its seamless integrations with popular productivity suites and real-time collaboration tools further streamline team planning and project visualization.
Key features:
Template library. Use professional templates, including org charts, flowcharts and Gantt charts, to quickly start your WBS.
Brainstorming tools. Capture your team members’ best thinking in real time with built-in brainstorming features like sticky notes and mindmaps.
Data-driven diagrams. Generate WBS diagrams from existing data within platforms like Jira.
Professional-looking output. Create polished, presentation-ready diagrams that enhance communication and alignment.
Who should use it: SmartDraw helps Project managers and teams looking for pre-built templates and who want to be able to generate a WBS from existing data or mind maps.
5. Creately
Creately is a visual collaboration platform that allows teams to create and easily share diagrams, mind maps, flowcharts and other visual documents.
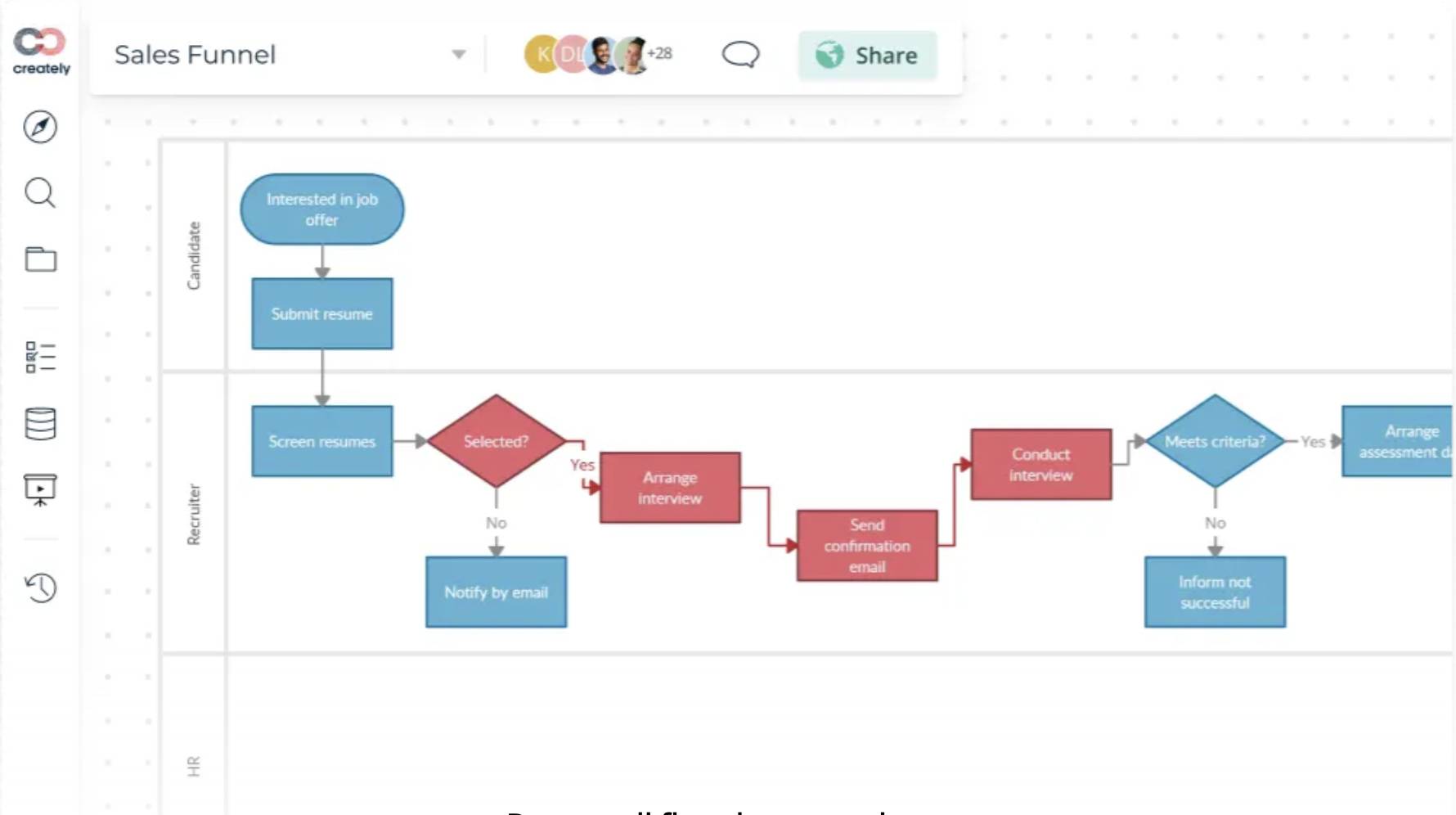
Source: Creately
The software provides a collaborative platform to manage and export WBS diagrams, simplifying project scope visualization and planning.
Key features:
Visual collaboration. Boost multi-user collaboration with @mentions, comments and the ability to embed context (e.g., documents and images) directly onto the canvas.
Template libraries. Create the work breakdown structure quickly with pre-built WBS templates.
Easy export. Export WBS diagrams in various formats (JPEG, PNG, SVG, PDF) to add to documents, presentations and other tools.
Editable permissions. Control who can view and edit your diagrams with customizable accessibility levels.
Who should use it: Creately is helpful for project managers who need to break down complex projects into visual components to present to stakeholders.
Final thoughts
A work breakdown structure offers a visual representation of all your project tasks so you can see exactly what you need to do to execute the project successfully. It also helps you create accurate project schedules and realistic project timelines and manage resources effectively.
A project management tool like Pipedrive makes creating a work breakdown structure easier. It allows you to organize tasks easily and quickly share the WBS with your project team.
Sign up for a free trial to see how Pipedrive can enhance your project management.





